Axicon lens
|
Substrate Material
|
UV Fused Silica
|
|
Diameter
|
12.7 mm or 25.4mm
|
|
Edge Thickness
|
5.0mm
|
|
Diameter Tolerance
|
+0/-0.1mm
|
|
Edge Thickness Tolerance
|
+0.01/-0.0mm
|
|
Center Thickness Tolerance
|
+0.01/-0.0mm
|
|
Apex Rounding Diameter(S1)
|
<1.5mm
|
|
Surface Quality(S1,S2)
|
40/20 Scratch-Dig
|
|
Surface Flatness(S2)
|
<λ/10@633nm
|
|
Surface Deviation(RMS)(S1)
|
<0.05um
|
|
Surface Roughnes(RMS)(S1)
|
<6 Å
|
|
Clear Aperture(S1,S2)
|
>90% of Diameter
|
|
Surface Deviation(RMS)(S1)
|
<0.05um
|
|
Surface Roughnes(RMS)(S1)
|
<6 Å
|
|
Clear Aperture(S1,S2)
|
>90% of Diameter
|
|
Angular Tolerance
|
±0.01°
|
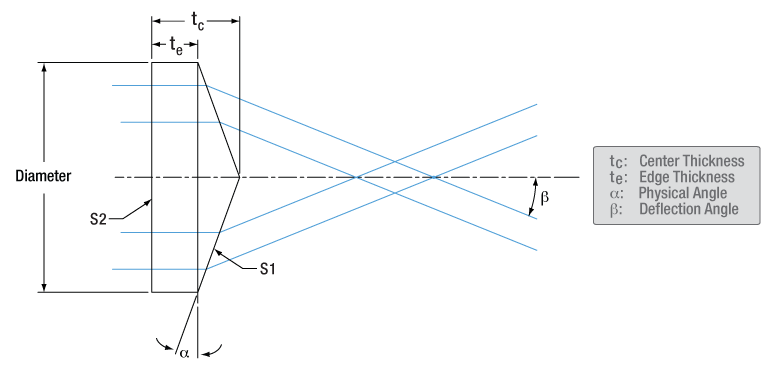
An axicon lens, also known as a rotationally symmetric prism, is a lens that features one conical surface and one plano surface with a different apex angle. They are commonly used to create a beam with a Bessel intensity profile or a conical, non-diverging beam. When converting a collimated beam into a ring, the plano side of the axicon should face the collimated source. These axicons are precisely manufactured from high-quality UV Fused Silica, making them ideally suited for high-power laser applications.
An axicon deflects light according to Snell's Law, which can be used to find the deflection angle:
where n is the index of refraction of the glass, α is the physical angle of the prism, and ß is the angle the deflected beam creates with the optical axis. Here, the refractive index of air is assumed to be 1.

